 |
 |
 | |
| Species: |
Monkey |
| Strain/breeder: |
Cynomolgus/Hartelust, NL |
| Sex: |
Male |
| Age: |
4 years |
| Study type: |
Intravenous infusion |
| Treatment: |
Oligonucleotide |
| Animal status: |
Scheduled death, end of study |
| Clinical findings: |
- |
| Organ: |
Kidney |
Macroscopic
finding(s): |
increased kidney weights |
| Staining: |
H&E |
| Literature: |
 |
Levine AA, Montheith DK, Leeds JM, et al. (1998) Toxicity of oligonucleotide therapeutic agents. In: Hanbook of experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 131, pp 169-210 |
 |
Henry SP, Bolte H, Auletta C, Kornbrust DJ (1997) Evaluation of the toxicity of ISIS 2302, a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide, in a four-week study in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicology 120: 145-155 |
 |
Monteith DK, Horner MJ, Gillett NA, Butler M, Geary R, Burckin T, Ushiro-Watanabe T, Levin AA (1999) Evaluation of the reanal effects of an antisense phosphotioate oligodeoxynucleotide in monkeys. Toxicol Pathol 27: 307-317 |
 |
Takakura Y, Oka Y, Hashida M (1998) Cellular uptake properties of oligonucleotides in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 8: 67-73 |
 |
Ganz MB, Albrightson C (1997) Experience with antisense oligodeoxy nucleotides in renal cells. Exp Nephrol 5: 175-179 |
|
|
 |
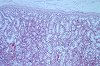
Fig. 1 (79k)

Fig. 2 (81k)
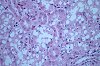
Fig. 3 (63k)
|
|
 |
Abstract
RENAL CHANGES IN CYNOMOLGUS MONKEYS AFTER 4-WEEK CONTINUOUS INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF OLIGONUCLEOTIDES
Aim of the study
To determine the toxicity of an intravenously administered oligonucleotide in a 4-week study.
Materials & methods
24-hour intravenous infusion of an oligonucleotide was performed on Cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) for four weeks using three dose levels (1mg, 4mg, 16mg per kg body weight per day). The control group received 0.9% NaCl solution intravenously. A 5-day post-operative recovery period was used. Two animals of each group had a 28 days recovery period. The animals were sacrified at term of study. Histopathological examination of organs was done according SOP guidelines.
Results
Clinically a very slight sedation was seen in the high dose group. Macroscopical examination showed a marked organ weight increase of kidney (p<0.01) and liver (not significant) in both medium and high dose level. Microscopy revealed a degeneration of tubular cells of kidney of high dose group with pigment deposits and vacuolization. Section from the liver showed necrosis, fatty infiltrates of von Kupffer cells with pigment deposits. The microscopic changes were nearly completely reversible in the animals with 28-day off-dose period after treatment.
Conclusions
Continuous intravenous infusion of oligonucleo-tides in the medium and high dose group resulted a typical vacuolar degeneration with pigment deposits in the kidney and liver. The changes are nearly reversible after 4 weeks of recovery.
case index | << previous case | next case >>
|
 |