 |
 | |
| Species: |
Rat |
| Strain/breeder: |
SD/Charles River |
| Sex: |
Male |
| Age: |
10 weeks |
| Study type: |
|
| Treatment: |
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS), 100µl, i.t. |
| Animal status: |
|
| Clinical findings: |
No clinical findings |
| Organ(s): |
Lung |
Gross
finding(s): |
No gross findings |
| Staining: |
H&E, Alcian blue-PAS |
| Literature: |
|
|
 |
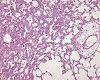
Fig. 1 (115k)
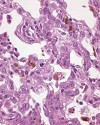
Fig. 2 (115k)
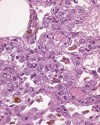
Fig. 3 (120k)
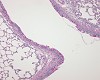
Fig. 4 (64k)
|
|
Abstract
LPS-induced lung lesions in rats
T. Wöhrmann1, L. Wollin2, K. Tuch1, and G. Bode1
1 ALTANA Pharma AG, Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Hamburg, Germany
2 Department of Pharmacology, Konstanz, Germany
Key words: LPS, lung, rats, COPD- like lesions, animal model
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by a progressive and largely irreversible limitation of airflow accompanied by chronic respiratory tract inflammation. There is an urgent need to improve present therapy by drugs with new modes of actions. To mimic some characteristic features of COPD symptoms in animals, a wide variety of animal models have been developed.
The bacterial endotoxin LPS was administered intratracheally into Sprague Dawley rats. 48 hours after instillation of LPS (100 µg/animal ~ 400 µg/kg) a pronounced multifocal, peribronchial inflammatory cell reaction with neutrophils and macrophages was observed. The inflammation was associated with proliferation of alveolar type II pneumocytes and goblet cell hyperplasia with marked mucus production in the bronchi.
To investigate the effects of different drugs on airway inflammation observed in COPD, the LPS- induced changes in the lung are an appropriate model at the moment. To further characterize these changes, immunohistochemical staining and morphometric analysis is currently being performed.
case index | << previous case | next case >>
|
 |